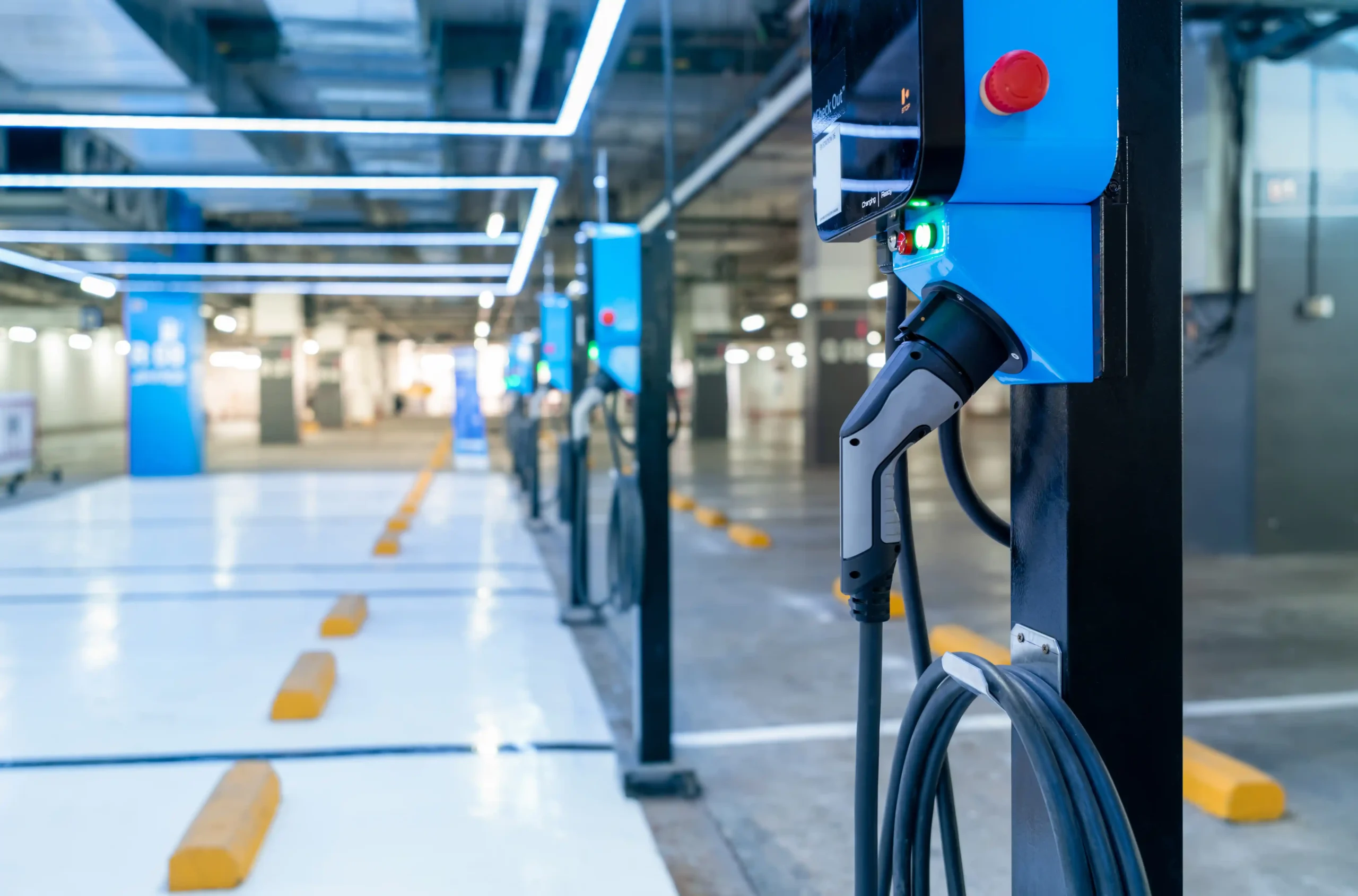
An electric vehicle (EV) uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It is powered either by rechargeable batteries or electricity from external sources, rather than a traditional internal combustion engine. To keep these vehicles operational, EV charging stations, also known as a charging point or electronic charging station (ECS), are part of the infrastructure that supplies electric energy to recharge plug-in vehicles, including electric cars, neighbourhood EVs, and plug-in hybrids.
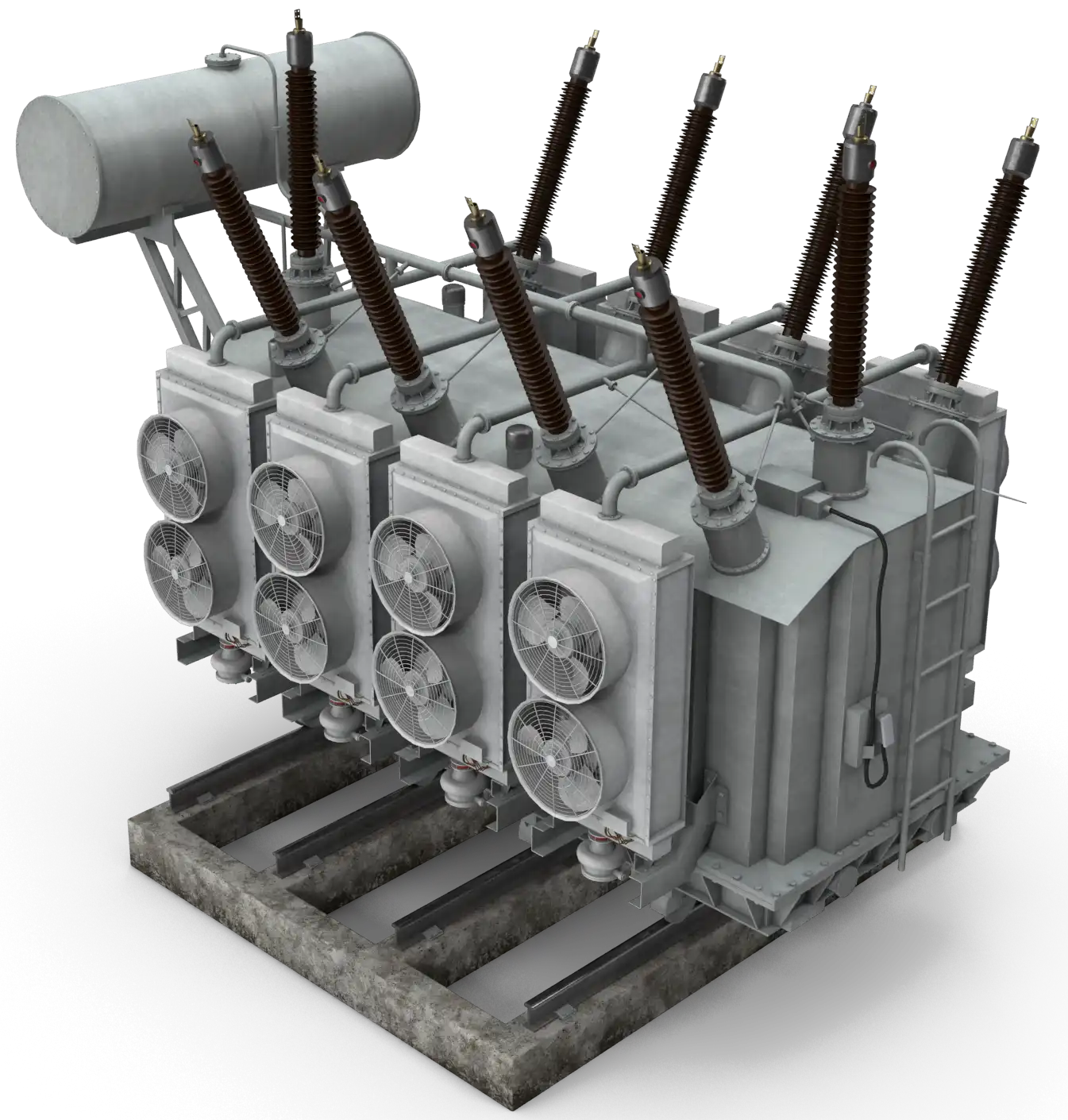
As the EV adoption increases, so does the need for sustainable charging infrastructure. This shift brings attention to the reliability and efficiency of charging networks, power distribution systems, and the electrical assets that support them. Most EV charging stations rely on power supplied through substations, making their capacity and reliability critical for large-scale deployment.